3. ACCESS RANGE FOR MONITORING
3.4 Data Link System (MELSECNET/B, (II)) Access Range for Monitoring
3 - 17
1
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES FOR
MONITORING
2
DEVICE RANGE
THAT CAN BE SET
3
ACCESS RANGE
FOR MONITORING
4
HOW TO MONITOR
REDUNTANT
SYSTEM
5
BUS CONNECTION
6
DIRECT
CONNECTION TO
CPU
7
COMPUTER LINK
CONNECTION
8
ETHERNET
CONNECTION
3.4 Data Link System (MELSECNET/B, (II)) Access
Range for Monitoring
Bus connection, CPU direct connection, Computer link connection
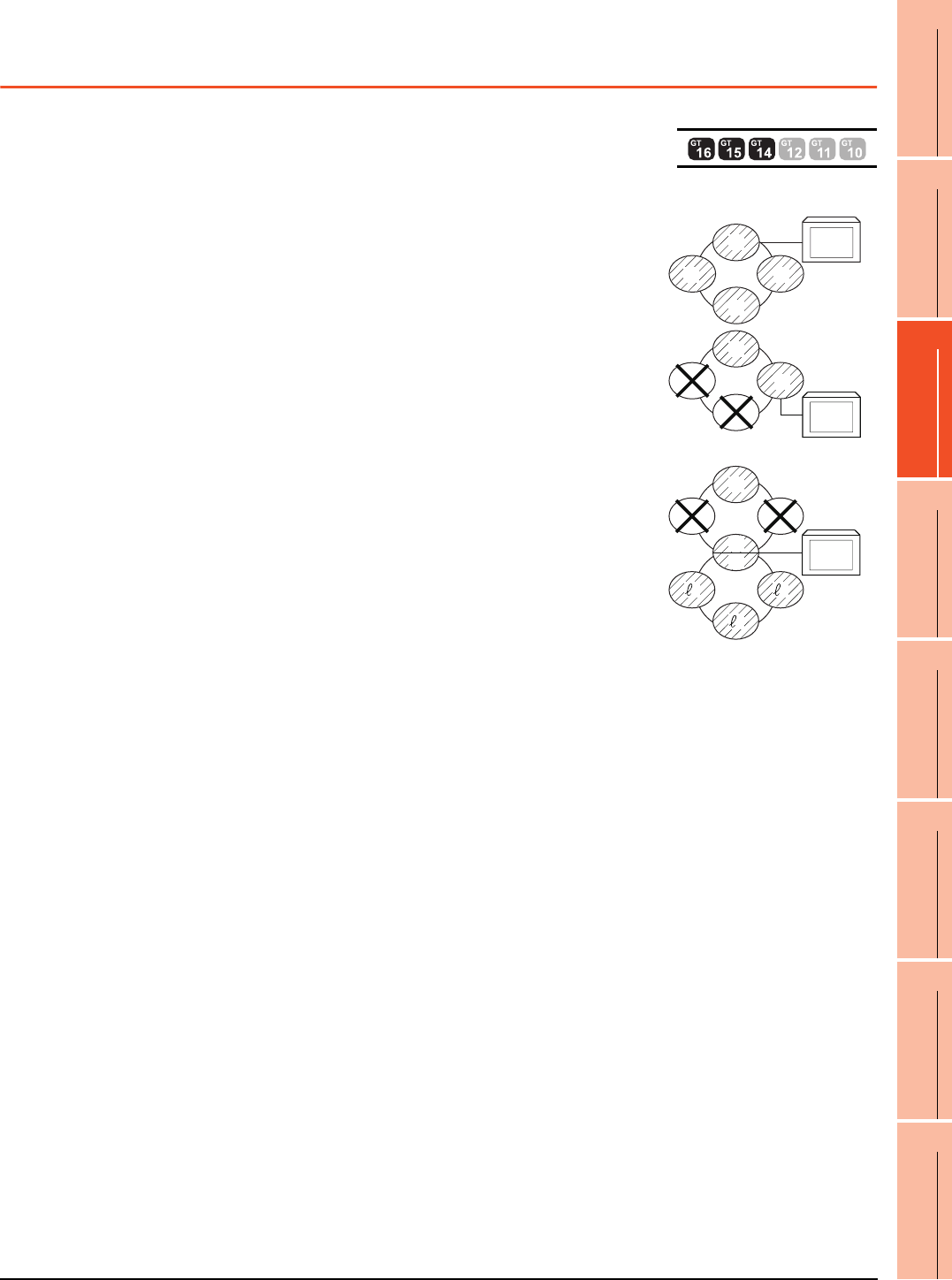
(1) When connecting to the master station
• Local stations can be monitored.
When the PLC CPU of the local station is QnACPU, devices other than B
and W that are allocated by the link parameter cannot be monitored.
(2) When connecting to the local station
• The master station can be monitored.
However, when the PLC CPU of the local station is QnACPU, devices other
than B and W that are allocated by the link parameter cannot be monitored.
• Other local stations cannot be monitored.
(3) When connecting to the master station on the third layer
• The master station on the second layer and local stations on the third layer
can be monitored.
However, when the PLC CPU of the local station is QnACPU, devices other
than B and W that are allocated by the link parameter cannot be monitored.
• Local stations on the second layer cannot be monitored.
Monitoring devices of other stations
If devices of other stations on the data link system are monitored, the display speed will be significantly reduced.
Therefore monitor the link relay (B) and link register (W) that are allocated by the link parameter.
L3
M
L1
L2
GOT
L1
L2
M
L3
GOT
GOT
L3
M
L1
L2
m
2
1
3


















