November 2004
Avaya Modular Messaging Concepts and
Planning Guide
A-1
A
Grade of service
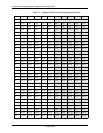
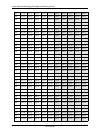
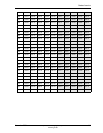
The tables in this appendix show the maximum busy hour traffic
supported by a given number of ports for each grade of service (GOS),
and the average number of ports in use during the busy hour.
Table A-1 uses the Erlang B and Erlang C models to provide information
on the port capacity in Erlangs, for each grade of service.
Note: Erlangs, CCS, and minutes are three different measures of
traffic. 60 minutes = 1 Erlang = 36 CCS.
The Erlang B model. The Erlang B model represents a scenario in which
incoming calls are not queued on the switch. If a caller calls when all
ports are busy, the caller hears a busy tone and the call is blocked.
GOS with Erlang B = probability of being blocked and thus busy tone
The Erlang C model. The Erlang C model represents a scenario in which
incoming calls are queued on the switch. The caller hears multiple rings if
all ports are in use, and the call is significantly delayed. The call is
eventually answered if the caller does not hang up.
GOS with Erlang C = probability of encountering a delay and thus ring
back. If there is a delay, the probability of delay will be more than 10% of
the average hold time (AHT).
Avaya Communication Manager with Q-Signaling (QSIG) integration
does not support queuing of calls when all ports are busy.