MSM80C154S/83C154S/85C154HVS
176
4.9.3 Cancellation of CPU power down mode (IDLE, PD) by interrupt signal
When idle mode (IDLE) and soft power down mode (PD) are cancelled by interrupt signal,
power down mode cancellation condition is determined by bit 5 (RPD) of the power control
register (PCON 87H) shown in Table 4-29.
When RPD is “0”, power down mode can be cancelled by interrupt signal and CPU executes
program from the interrupt address only when the CPU has been set to interrupt enable
status.
And when RPD is “1”, power down mode can be cancelled and resumes execution from the
next address after the stop address if “1” is set in the interrupt flag by interrupt signal even
when the CPU is in interrupt disable mode.
The conditions for cancellation of power down mode by interrupt signal can thus be specified
by the RPD content.
Table 4-29 Power control register (PCON 87H)
Bit
Set
SMOD HPD RPD
—
GF1 GF0 PD IDL
76543210
•
4.9.3.1 Cancellation of CPU power down mode (IDLE, PD) from interrupt address
To cancel idle mode (IDLE) or soft power down mode (PD) and resume execution from the
interrupt address, an interrupt is specified in the interrupt enable register (IE 0A8H) prior to
setting CPU power down mode and “0” is set in bit 5 (RPD) of the power control register
(PCON 87H).
All six interrupts can be used to cancel idle mode. The interrupt conditions are satisfied when
“1” is set in the specified interrupt flag in TCON, T2CON, or SCON. Clock signals are then
passed to the CPU, and execution is commenced from the interrupt address.
Soft power down mode (PD) can be cancelled by four different interrupts - external interrupts
0 and 1, and timer interrupts 0 and 1. (Timer/counters 0 and 1 are operated in external clock
mode.)
The external interrupts are generated by “0” level being applied to either the INT0 or INT1 pin.
When the specified interrupt flag in TCON is set to “1” to satisfy the interrupt conditions,
XTAL1·2 operation is commenced, and the program is executed from the interrupt address.
When the interrupt routine is completed, the program returns to the next address after the stop
address.
If all interrupts have been disabled, however, CPU power down mode cannot be cancelled
from the interrupt address by this method. A “1” reset signal must be applied to the RESET
pin and execution commenced from address 0 in this case. The equivalent circuit involved
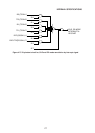
in CPU power down mode cancellation by interrupt is shown in Figure 4-75, and the CPU
power down mode (PD, HPD) cancellation time charts are shown in Figures 4-76 thru 4-79.