Byte Ordering and Bit Coding Convention
xii Interphase Corporation
Byte Ordering and Bit Coding Convention
The PCI bus uses the Little Endian Byte ordering: byte 0 in a 32-bit word is the Least
Significant Byte (LSB) from an arithmetic point of view and is noted D(7:0). The PowerPC
architecture uses the Big Endian Byte ordering: byte 0 in a 32-bit word is the Most
Significant Byte (MSB) from an arithmetic point of view and is noted D(31:24).
The PowerPC architecture uses the very unusual Little Endian Bit convention, where bit 0
is on the left and is the most significant bit. Unless otherwise noted, this document does not
use this convention. Instead, it uses the classical bit coding convention, where bit 0 (on the
right) is the least significant bit and bit i is the 2
i
weight bit. This is the Big Endian Bit
convention. This coding convention applies to data, addresses, and bit fields. In the
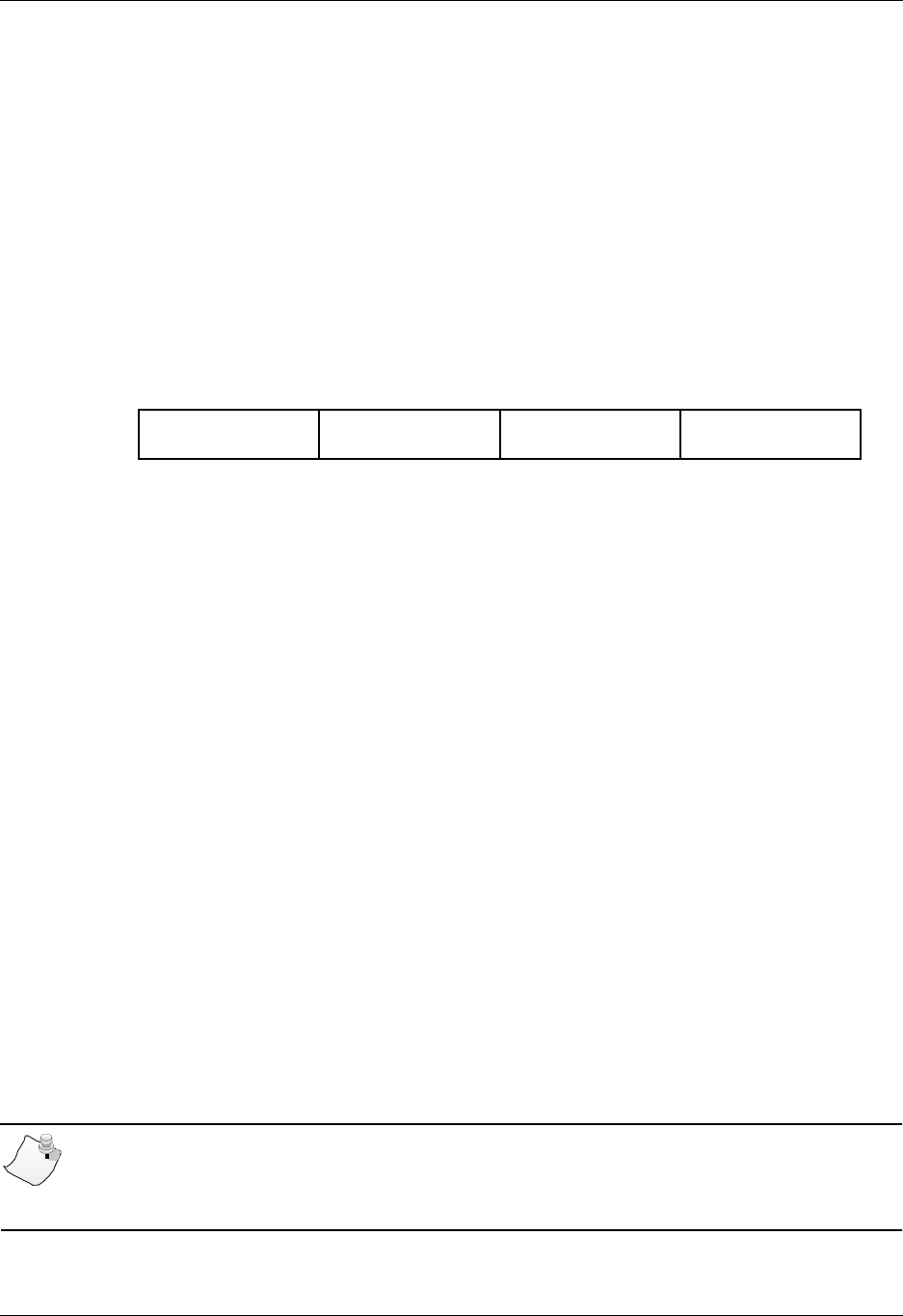
following figure, MSB means Most Significant Byte and LSB Least Significant Byte:
The standard C convention is used to identify the numeric format of arithmetical values:
• No prefix for decimal values
• 0x prefix for a hexadecimal value
For example 0x12 = 18.
Type Definition
Only a few basic types are used:
• byte: unsigned, coded as 8 bits
• word: unsigned, coded as two contiguous bytes, most significant first
• dword: unsigned, coded as two contiguous words, most significant first
Code Examples
This document provides several algorithm descriptions presented in PowerPC assembly
language and in C language.
Icon Conventions
Icons draw your attention to especially important information:
NOTE
The Note icon indicates important points of interest related to the current subject.
06% /6%