9-2
Cisco MDS 9000 Family NX-OS Quality of Service Configuration Guide
OL-29284-01
Chapter 9 Configuring Port Tracking
Guidelines and Limitations
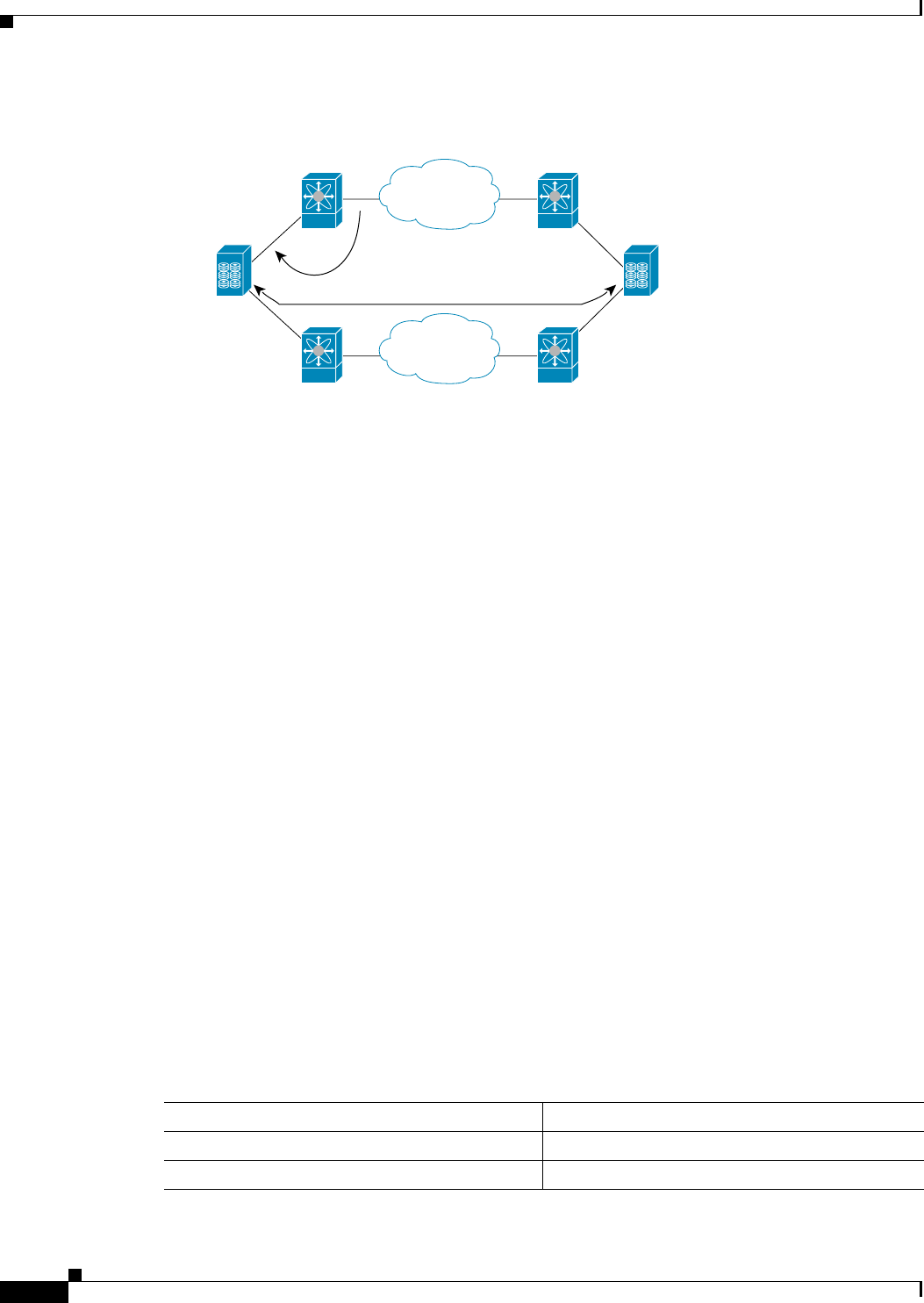
Figure 9-1 Traffic Recovery Using Port Tracking
The port tracking feature monitors and detects failures that cause topology changes and brings down the
links connecting the attached devices. When you enable this feature and explicitly configure the linked
and tracked ports, the Cisco NX-OS software monitors the tracked ports and alters the operational state
of the linked ports on detecting a link state change.
The following terms are used in this chapter:
• Tracked ports—A port whose operational state is continuously monitored. The operational state of
the tracked port is used to alter the operational state of one or more ports. Fibre Channel, VSAN,
PortChannel, FCIP, or a Gigabit Ethernet port can be tracked. Generally, ports in E and TE port
modes can also be Fx ports.
• Linked ports—A port whose operational state is altered based on the operational state of the tracked
ports. Only a Fibre Channel port can be linked.
Guidelines and Limitations
Before configuring port tracking, consider the following guidelines:
• Verify that the tracked ports and the linked ports are on the same Cisco MDS switch.
• Do not track a linked port back to itself (for example, Port fc1/2 to Port fc2/5 and back to Port fc1/2)
to avoid recursive dependency.
• Be aware that the linked port is automatically brought down when the tracked port goes down. Be
aware that the linked port is automatically brought down when the tracked port goes down.
Default Settings
Table 9-1 lists the default settings for port tracking parameters.
FCFCFC FCFC
WAN or
MAN
WAN or
MAN
Direct link 1
ISL2
X
X
120490
Ta b l e 9-1 Default Port Tracking Parameters
Parameters Default
Port tracking Disabled.
Operational binding Enabled along with port tracking.
