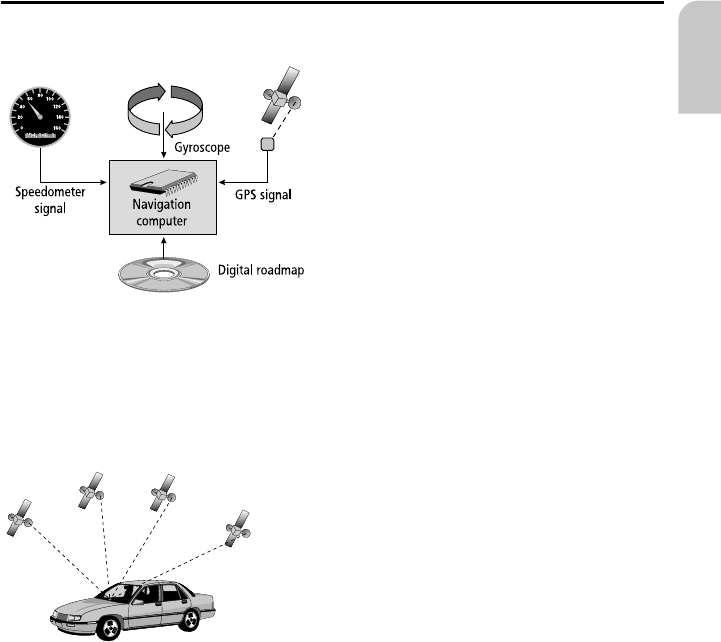
How does the navigation system work?
The position and movements of the vehicle
are recorded by the navigation system’s
sensors. The distance travelled is determined
by the vehicle speedometer signal, rotary
motion in curves is detected by a gyro sensor
(inertial compass). The position is determined
via the GPS (Global Positioning System)
satellites.
The position can be calculated within a range
of approx. 10 m by comparing the sensor
signals with the digital map on the
navigation CD.
Important notes on the function of your navigation radio
In principle, the system is functional with poor GPS reception, although the accuracy of
the positioning may be impaired by poor or interrupted GPS reception or errors can
occur in the determination of the position, which result in incorrect position reporting.
Start-up characteristics
If the vehicle is parked for longer periods of time,
the satellites continue their orbit. After the
ignition is switched on, it may take several
minutes until the navigation system receives
signals from sufficient satellites for evaluation.
During the start-up sequence, it is possible that the navigation system will report:
“You are leaving the digitised area”. The navigation system assumes that the vehicle is
located outside a digitised area. If other roads exist in this area, the navigation system
may issue incorrect messages. The navigation system assumes that the vehicle is located
on another road.
Comments
After transport of the vehicle by train or ferry, the navigation system may require a
few minutes for exact positioning.
After disconnecting the vehicle battery, up to 15 minutes may be required for exact
positioning. For this, the vehicle must be outdoors and the system must be switched on
in order to receive transmissions from the GPS satellites.
GENERAL INFORMATION
11
English


















