ACOUSTICS - BACKGROUND INFO
36
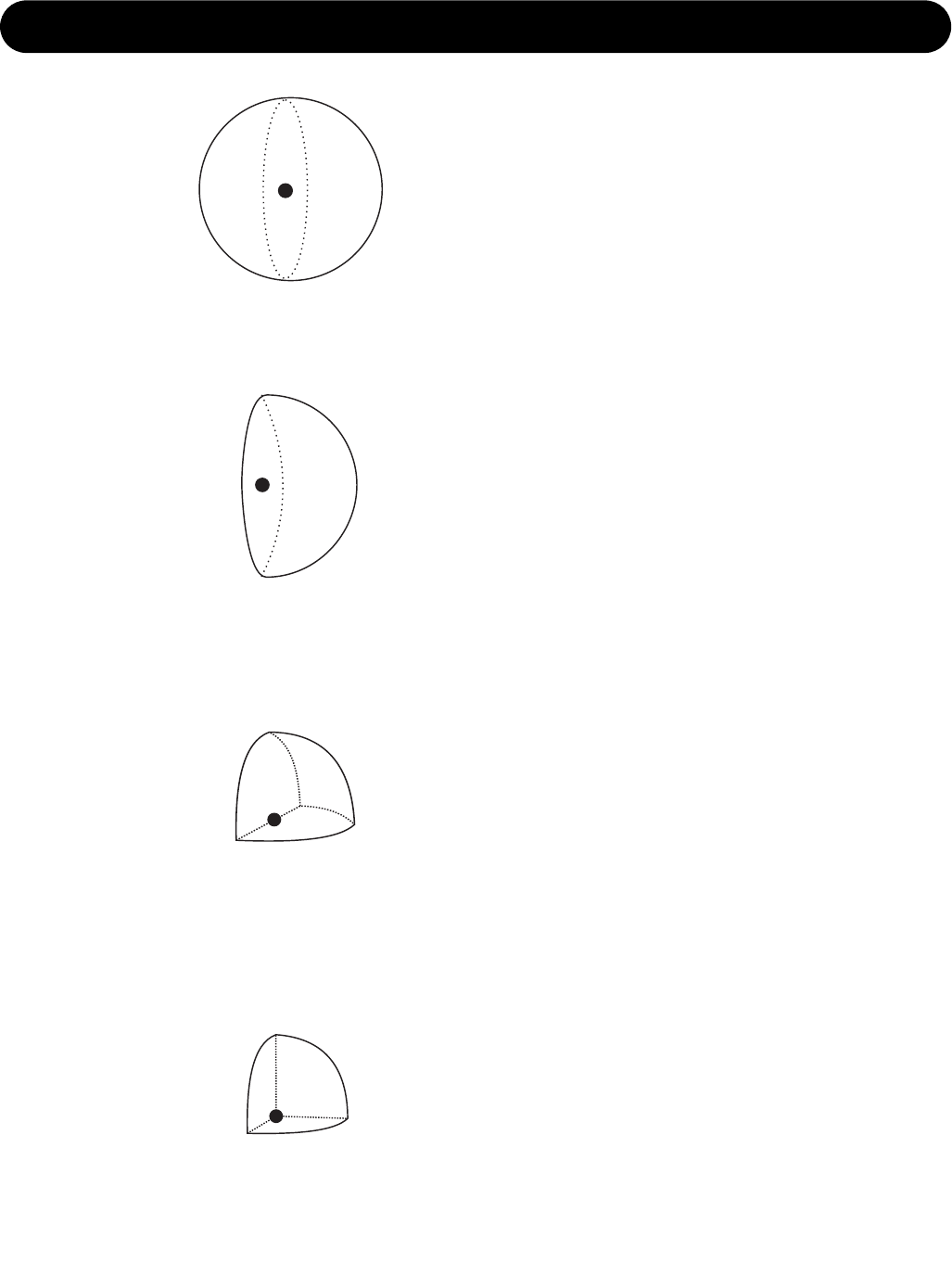
At low frequencies a monitor can be considered
as to radiate the sound energy in all directions.
This is also called a 4 π radiation.
When placing the monitor close to a solid
boundary - for instance a wall - the sound
energy that should have been radiated in the
direction of the wall instead is radiated into the
free half space. Hence the sound pressure is
doubled in the half space, which yields +6 dB.
This is also called a 2 π radiation.
Placing the monitor against two boundaries - for
instance in a corner limited by two walls - it is
now radiating to the quarter space. Now the
sound pressure is doubled twice, which yields
+12 dB.
This is also called a π radiation.
Placing the monitor against three boundaries -
for instance in a corner limited by the floor and
two walls - the sound is radiated into 1/8 of the
space. Compared to free space, the sound
pressure now is increased by 18 dB.
This is also called π/2 radiation.
In practice the placement close to boundaries will influence the frequency
range below 125-150 Hz.


















