Administrator Guide
90
Working from a Linux Computer
The Appliance is ready for use from clients using NFS as soon as it is installed on
your network. Use the Appliance as you would any other drive or server on the
network:
• Connect to the appliance by IP address and directory path to a local mount point.
• Create and save shared files in folders and shares on the appliance.
• Backup files stored on the appliance.
• Create KDE/GNOME desktop icons and symbolic links for convenience and
faster access.
• To handle Samba (Windows) connections, you can also use the
LinNeighborhood utility with a convenient GUI.
Mounting a share on the appliance (Linux and UNIX)
You must know the appliance IP address and public mount point in order to
connect to the appliance. Once the IP address and target mount point are
established, the appliance is accessed using a mount command with the target IP
address, target mount point, and local mount point, in the form of ‘mount ip-
address:/target-directory-path /local-mount-point’. The target directory path
depends on how the appliance disks are configured. If the appliance has been
configured with a static IP address, ask the administrator for this address to
connect to the server. If the appliance is set to obtain a DHCP IP address
automatically, either get the IP address from the DHCP manager application, or
ask the system administrator.
Note
NFS mounts only succeed with public shares on the server. Private shares
should be accessed through Windows or Macintosh clients.
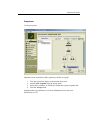
To create a local mount
1. From a Linux console, type: mkdir [directory name] <Enter>
For example, if you want to create a directory named testdir, you would type:
mkdir testdir
And then press <Enter>
Type: ls [directory name] <Enter>
The contents of the directory display; it is empty.