Administrator Guide
75
6 Configuring Storage Settings
Managing RAID
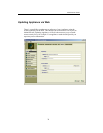
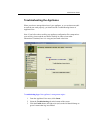
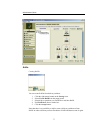
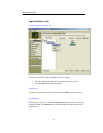
Through ApplianceView, you can create, edit, deconstruct, and view a RAID.
Available RAID levels
Three types of RAID configurations are available for the data partition. These
RAID levels can be used on a multi-drive appliance, whether or not a hardware
RAID card is installed. If there is no hardware RAID card installed, you can use
software RAID. It is important to note that for a two-drive appliance, the only
RAID levels available are 0 and 1. For an appliance with three or more drives,
RAID levels 0, 1, and 5 are available.
RAID 0: Single Large Volume
This type of RAID is also referred to as striping. RAID 0 interleaves
blocks of data between several drives. Even though multiple drives
exist in the array, to the user a RAID 0 appears as a single large
volume. It is important to understand however, that there is no form of
data backup when using a RAID 0. If a single drive fails, you will lose
the entire array. This type of RAID should not be used for mission
critical data. RAID 0 is available for any system with two or more
drives.
RAID 1: Mirroring
This type of RAID is used to create a mirror copy of the information
contained on one or more of the disks. In this method, a mirror is
created for each drive containing data. For example, in a two drive
RAID 1 setup, both drives contain the exact same data. Since there is
100% redundancy, there is no risk of losing data if one drive fails.
RAID 1 is available for any system with two or more drives.
RAID 5: Disk Striping with Distributed Parity
This type of RAID features both striping and redundancy. This type of
RAID uses a technique called distributed parity, which allows data to
be recovered if one drive in the RAID fails. In addition, data blocks
are interleaved evenly across the drives in parity bits. RAID 5 is only
available for systems that have three or more drives.