Appendix
The DVCAM format was developed as a more reliable and higher end
format than the consumer DV format. Here we explain the DVCAM and
DV formats: the differences, compatibility and limitations on editing.
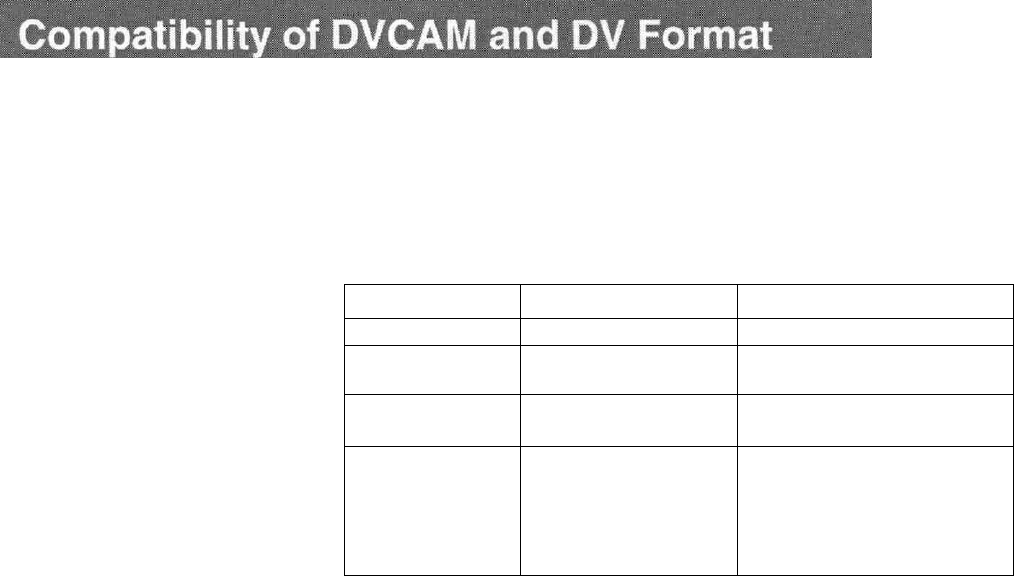
Differences between DVCAM and DV format
Item
Track pitch
Audio sampling
frequency
Audio recording
mode
1)
Time code system
DVCAM
15
urn
12
bit:
32
kHz
16
bit:
48
kHz
Lock mode
NTSC; SMPTE time
code (DF/NDF/including
user bits)
3
'
PAL; EBU time code
(including user bits)
3
'
DV
10
[im
12
bit:
32
kHz
16 bit: 32 kHz, 44.1 kHz, 48 kHz
2
'
Unlock mode
Drop frame mode (NTSC)
without user bits
There are two modes for audio recording; Lock mode and Unlock mode. In
Lock mode, the sampling frequencies of audio and video are synchronized. In
Unlock mode, which the consumer DV format adopts, the two sampling
frequencies are independent. The lock mode maintains high compatibility with
the higher formats and is more effective than unlock mode in digital processing
and smooth transition during audio editing.
This unit cannot record in DV format with 16 bit - 32 kHz or 44.1 kHz.
The user bits cannot be set on this unit.
1)
2)
3)
Appendix
55