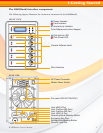
RAIDBank5 Owner’s Manual
16
RAID 10 (Striped Mirror)
RAID 10 combines striping with disk mirroring.
RAID Level 10 combines the fast performance
of Level 0 with the data redundancy of Leve1 1.
In this configuration, data is distributed across
several disk drives, similar to Level 0, which
are then duplicated to another set of drive for
data protection. RAID 10 provides the highest
read/write performance of any of the Hybrid
RAID levels, but at the cost of doubling the
required data storage capacity.
Pros: Fastest read/write performance of any of the Hybrid RAID levels. Fault tolerant
Cons: Requires double the raw data storage capacity
RAID 3
RAID 3 provides disk striping and complete
data fault tolerance though a dedicated parity
drive. RAID 3 breaks up data into smaller
blocks, calculates parity on the blocks, and
then writes the blocks to all but one drive in
the array. The parity data created is then written
to the last drive in the array. If a single drive
fails, data is still available by computing the
inverse operation on the data and parity of the
contents corresponding strips of the surviving
member disk. RAID 3 is best for applications that require very fast large block data transfer
rates or long data blocks.
Pros: Very good large file transfer performance. Fault tolerant.
Cons: Not well suited for transaction processing or other I/O request-intensive applications.
RAID 5
RAID 5 is sometimes called striping with parity
at byte level. In RAID 5, the parity information
is written to all of the drives in the subsystems
rather than concentrated on a dedicated parity
disk. If one drive in the system fails, the parity
information can be used to reconstruct the data
from that drive. All drives in the array system
can be used to seek operation at the same time,
greatly increasing the performance of the RAID
system. RAID 5 is the most often implemented
RAID algorithm in RAID arrays.
Pros: Very good general transfer performance. Fault tolerant.
Cons: Can be slower then RAID 3 at large size file transfers
2-Understanding RAID