RAIDBank5 Owner’s Manual
15
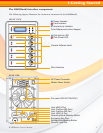
RAID 0 (Striping)
This RAID algorithm writes data across multiple disk drives instead of just one disk drive. RAID
0 does not provide any data redundancy, but
does offer the best high-speed data throughput.
RAID 0 breaks up data into smaller blocks and
then writes a block to each drive in the array.
Pros: Disk striping enhances both read and
write performance because multiple drives
are accessed simultaneously
Cons: The reliability of RAID Level 0 is less than
any of its member disk drives due to its lack
of redundancy.
Disk Spanning
This RAID algorithm writes data to multiple disk
drives sequentially. Spanning does not provide
any data redundancy, and is only as fast as a
single disk drive.
Pros: Disk spanning provides a large logical
volume from multiple smaller disks. The
entire disk capacity is available for user
access.
Cons: No fault tolerance, speed equivalent to a
single disk.
RAID 1 (Disk Mirroring, Cloning)
RAID 1, also known as “disk mirroring”, distributes
duplicate data simultaneously to 2 disk drives.
Pros: RAID 1 offers extremely high data reliability
as all the data is redundant. If one drive
fails, all data (and software applications)
are preserved on the other drive. Read
performance may be enhanced as the
array controller can access both members
of a mirrored pair in parallel.
Cons: RAID 1 volume requires double the raw
data storage capacity. During writes, there will be a minor performance penalty when
compared to writing to a single disk.
A0
A1
A2
A3
B0
B1
B2
B3
C0
C1
C2
C3
D0
D1
D2
D3
Disk Spanning
2-Understanding RAID