DIGITAL RADIO GUIDE TERRESTRIAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS - HD RADIO
47
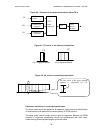
The flow of service content through the HD Radio broadcast system is as follows:
• Service content enters the HD Radio broadcast system via Service Interfaces;
• Content is assembled for transport using a specific protocol;
• It is routed over logical channels via the Channel Multiplex; and
• It is waveform modulated via the Waveform/Transmission System for over-the-air
transmission.
The system employs coding to reduce the sampled audio signal bit rate and baseband
signal processing to increase the robustness of the signal in the transmission channel.
This allows a high quality audio signal plus ancillary data to be transmitted in adjacent
frequency partitions and at low levels that do not interfere with the existing analog signals.
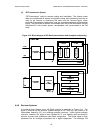
4.4.4 Core Services
(1) Main Program Service (MPS)
The Main Program Service (MPS) is a direct extension of traditional analog radio.
MPS allows the transmission of existing analog radio-programming in both analog
and digital formats. This allows for a smooth transition from analog to digital radio.
Radio receivers that are not HD Radio enabled can continue to receive the
traditional analog radio signal, while HD Radio receivers can receive both digital
and analog signals via the same frequency band. In addition to digital audio, MPS
includes digital data related to the audio programming. This is also referred to as
Program Associated Data (PAD).
(2) Station Information Service (SIS)
The Station Information Service (SIS) provides the necessary radio station control
and identification information, such as station call sign identification, time and
location reference information. SIS can be considered a built-in service that is
readily available on all HD Radio stations. SIS is a required HD Radio service and
is provided dedicated bandwidth.
(3) Advanced Application Services (AAS)
Advanced Application Services (AAS) is a complete framework in which new
applications may be built. In addition to allowing multiple data applications to share
the Waveform/ Transmission medium, AAS provides a common transport
mechanism as well as a unified Application Programming Interface (API). On the
transmission side, broadcasters utilize the common AAS interface to insert
service(s) into their signal; receiver manufacturers utilize the AAS ‘toolkit’ to
efficiently access these new services for the end-user. AAS includes separate
audio programming such as reading services and other secondary aural and data
services.