DIGITAL RADIO GUIDE TERRESTRIAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS - DRM
15
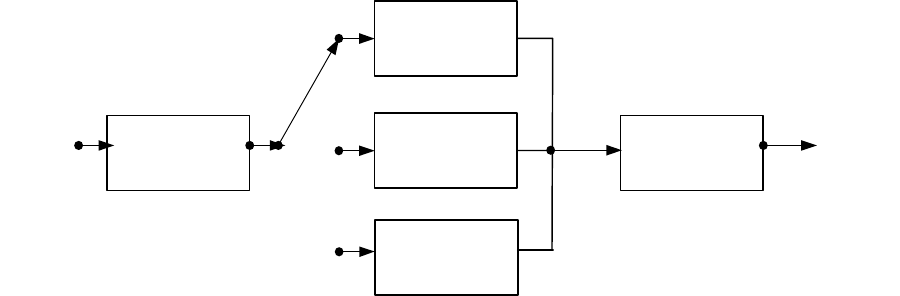
DRM Source Decoding
super
framing
demux
AAC
Decoder
CELP
Decoder
SBR
Decoder
bit
stream
Audio
output
HVXC
Decoder
Extensive tests on these codecs at the sampling rates and resulting “bandwidths”
have determined that AAC and especially AAC with SBR produce a perceived
audio quality to listeners that is effectively the equivalent of monophonic FM in a 9
or 10 kHz channel. HVXC produces intelligible speech quality with bit rates of 2 to
4 kbps for HVXC and CELP produces excellent speech quality using around 8 kbps.
All of these codecs are a part of the MPEG-4 audio standard.
SBR (Spectral Band Replication) is a special means of enhancing the perception of
a spectrally truncated low band audio signal by utilizing, on a dynamic basis, the
spectral content of the low band information to simulate the missing higher band
behaviour. This requires about 2 kbps and therefore does not seriously subtract
from a 20 to 25 kbps AAC output.
In concept, the technique is not complicated. Consider a violin as an example. A
string stimulated by a bow and the placement of a finger on the string produces a
fundamental frequency and harmonics characteristic of a violin. These frequencies
can go as high as the audibility of the human ear – say somewhere between 15
and 20 kHz.
For a 9 or 10 kHz channel, the AAC sampling and processing of the violin’s output
can only cover the lower part of the audio spectrum, for example not higher than 6
kHz. The SBR algorithm examines this lower band spectrum on a dynamic basis
and infers what the “missing” higher audio frequency “harmonics” probably are.
The level of re-inserted harmonics depends on the 2 kbps SBR helper signal which
describes the shape of the spectral energy in the original signal before truncation
for AAC coding stereo (which uses an additional 2 kbps of SBR). From the
standpoint of a listener, the combined audio output sounds like 15 kHz audio rather
than 6 kHz audio.
(4) Multiplexing, including special channels and energy dispersal
This section refers to the left side of Figure 4.1 through “energy dispersal”, not
including the DI and audio/data encoding portions.
As noted in Figure 4.1, the DRM system total multiplex consists of 3 channels: the
MSC, the FAC and the SDC. The MSC contains the services – audio and data. The
