JURISDICTION TO JURISDICTION.
G-Technology, a
division of Hitachi
Global Storage
Technologies
Tel: (310) 449-4599
Fax: (310) 449-4670
support@g-technology.com
G-Technology by Hitachi Global Storage Technologies © 2010. All
rights reserved. G-DRIVE, G-RAID, G-SAFE, and G-SPEED are
registered trademarks of G-Technology by Hitachi GST. Apple, Mac,
Macbook, Macbook Pro and the Mac logo are trademarks of Apple,
Inc. Hitachi Global Storage Technologies and Hitachi Inspire the
Next are trademarks of Hitachi Ltd. G-Technology is a trademark of
Hitachi Global Storage Technologies. All other trademarks are the
property of their respective owners. Hitachi Global Storage
Technologies trademarks are authorized for use in countries and
jurisdictions in which Hitachi has the right to use, market and
advertise the brands. The Travelstar trademark is authorized for use
in the Americas, EMEA and the following Asia-Pacic countries and
jurisdictions: Australia, Hong Kong, Japan, New Zealand, South
Korea and Taiwan. Contact Hitachi for further information. Hitachi
shall not be liable to third parties for unauthorized use of Hitachi
trademarks.
One gigabyte (GB) is equal to one billion bytes and one terabyte
(TB) equals 1,000 GB (one trillion bytes). Accessible capacity will
vary from the stated capacity due to formatting and partitioning of
the hard drive, the computer’s operating system, and other factors”
For G-Technology by Hitachi products less than 1TB: “One gigabyte
(GB) is equal to one billion bytes when referring to hard drive
capacity. Accessible capacity will vary depending on the operating
environment and formatting.
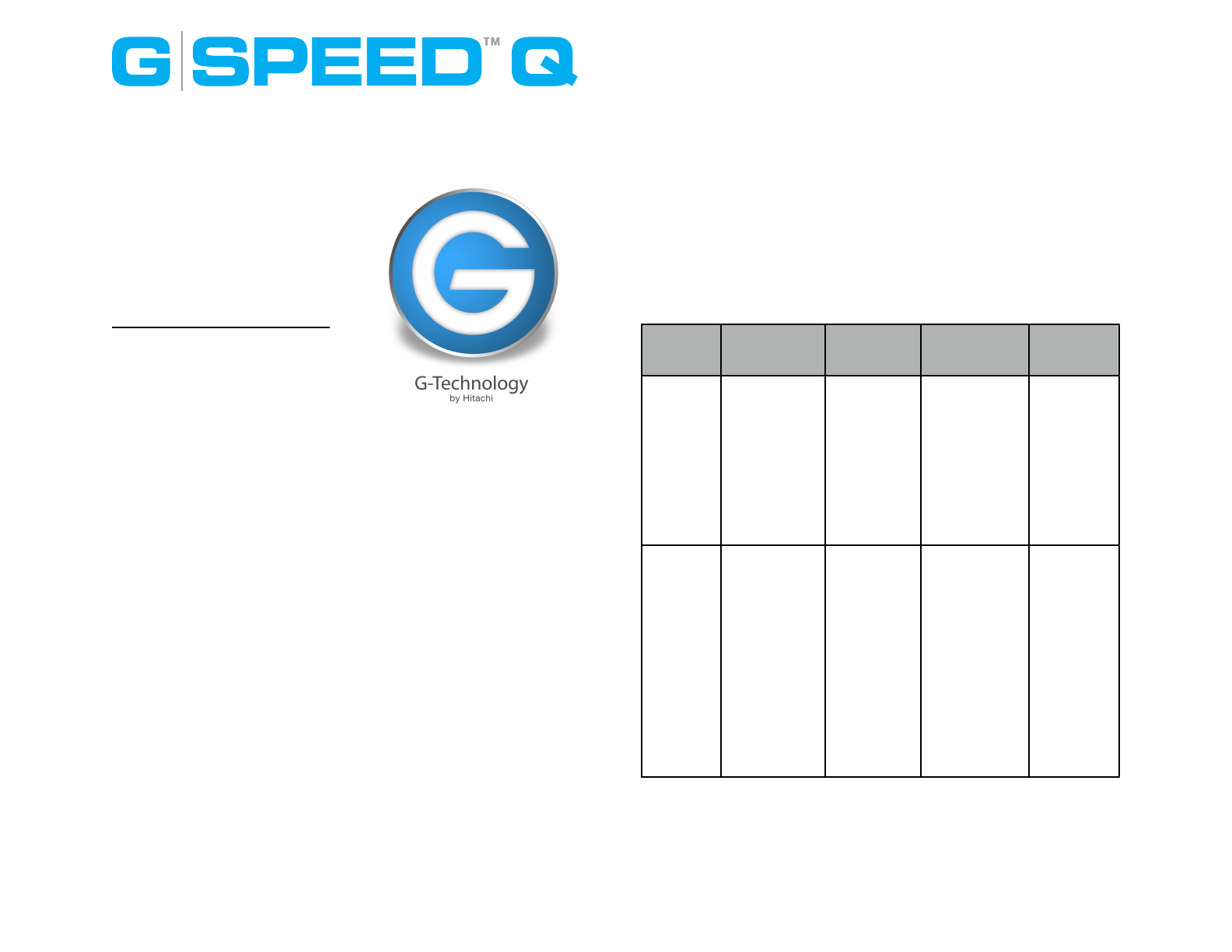
Appendix A: RAID Levels Explained
The following chart will help you understand the difference
between different RAID levels available for G-SPEED Q.
RAID
Level
Description
Advantage
Disadvantage
Ideal For
0
Disk striping
Offers the
highest
performance
and a useable
storage
capacity of
100% of total
available
storage
capacity
No fault
tolerance - failure
of one drive in
the array results
in complete data
loss
Content
creation
applications
requiring
highest
storage
capacity and
best
performance.
5
Disk striping
with
distributed
parity
High read
performance,
medium write
performance
with data
protection in
case of a drive
failure.
Useable storage
capacity equals
total capacity of
all drives in the
array less the
capacity of one
drive.
For example, a 4x
1TB RAID 5 yields
a useable
capacity of 3 TB.
Disk failure
results in drop in
performance
Content
creation
applications
requiring
data
protection
14